What is pH, and why is it Important
pH is an essential concept in chemistry, biology, and various industries. Understanding pH is crucial for assessing the acidity or alkalinity of solutions, impacting everything from agriculture to water quality and food safety. In this article, we will explore what pH is, why it’s important, and how it affects multiple applications in everyday life.
What is pH?
pH is a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of a solution. It is expressed on a scale of 0 to 14, where 7 is considered neutral. A pH below 7 indicates acidity, while a pH above 7 indicates basicity (alkalinity). The scale is logarithmic, meaning that each whole number represents a tenfold change in acidity or alkalinity. For example, a solution with a pH of 4 is ten times more acidic than a solution with a pH of 5.
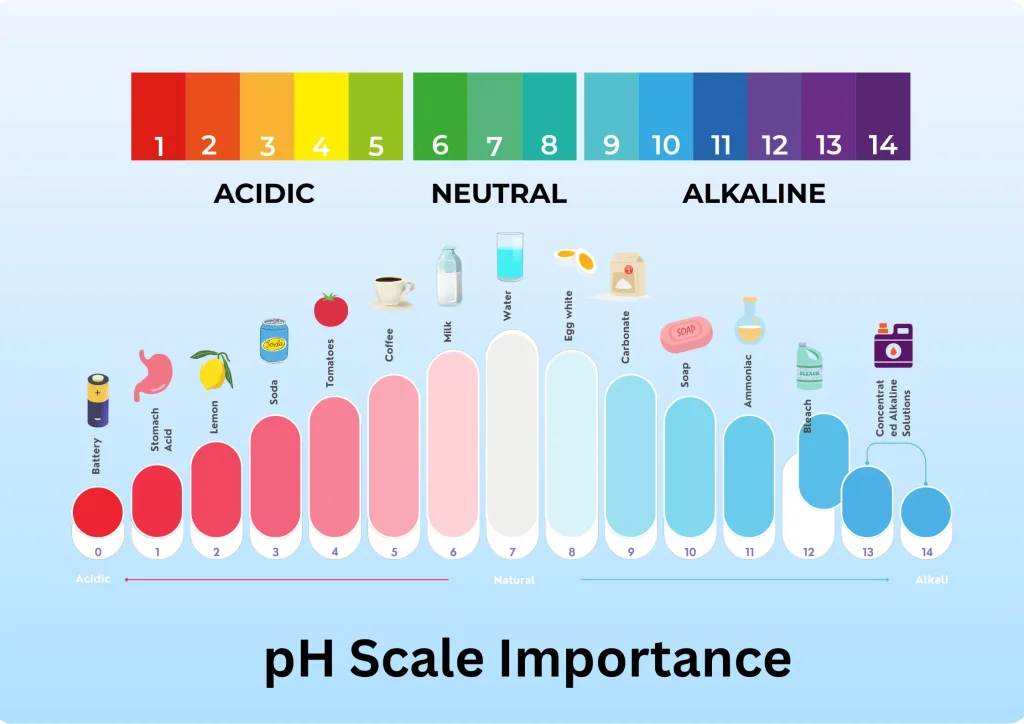
Why is pH Important?
pH plays a pivotal role in many biological, environmental, and industrial processes.
- Environmental Health: pH affects water chemistry, influencing aquatic life survival. Extreme pH levels in water can harm ecosystems, disrupt plant growth, and affect human health.
- Human Health: Our body maintains a stable pH, such as the highly acidic environment of the stomach (pH 1.5-3.5) for digestion and the slightly acidic skin (around pH 5.5) for protection against bacteria.
- Food Safety: pH levels in food impact its preservation, taste, and microbial activity. For example, food processing like pasteurization requires specific pH levels to ensure safety and prevent spoilage.
What Industries & Applications Need Accurate pH, & Why?
pH monitoring is critical in various industries. Accurate pH control ensures safety, quality, and effectiveness in many fields.
Wastewater Treatments
pH plays a critical role in water treatment processes. It ensures that harmful metals, such as copper and lead, don’t contaminate water supplies. pH levels in wastewater must be managed to facilitate chemical and microbial reactions for effective water purification.
Aquaculture & Aquatic Systems
pH is essential for the health of aquatic life. Fish and other organisms are sensitive to pH fluctuations. A pH range of 6.5-9.0 is optimal for most aquatic species. Low or high pH levels can harm aquatic ecosystems, disrupting reproduction and growth.
Swimming Pools & Spa Maintenance
For maintaining clean and safe swimming pools and spas, pH levels must be kept within a narrow range (7.2-7.8). Too high or too low pH can irritate the skin and eyes, or reduce chlorine’s disinfectant properties.
Hydroponics: Agriculture & Gardening
In hydroponics, the pH of water directly impacts plant growth. Maintaining the correct pH ensures optimal nutrient availability. For most plants, a pH range of 6.0 to 7.0 is ideal for healthy growth.
Food & Beverage Industry
In the food industry, pH affects taste, preservation, and safety. Low pH levels are used to prevent bacterial growth in dairy products like yogurt and cheese, while higher pH values can indicate spoiled meat. Accurate pH measurement is crucial for food safety and quality.
How to Measure pH?
pH can be measured using several methods, each with varying levels of accuracy and ease of use.
Colorimetric Methods
Colorimetric methods use pH indicators or litmus paper to visually determine pH. These methods are simple but less precise. The color change on the paper corresponds to a pH value, making this method ideal for basic tests.
Electrochemical Methods
Electrochemical methods, like pH meters, offer more accuracy and are used in scientific and industrial settings. These meters work by measuring the difference in voltage between a pH-responsive electrode and a reference electrode. pH meters are ideal for environments where precision is necessary.
Key pH Ranges for Different Applications
- Soil pH: Most crops grow best in soil with a pH of 6.0-7.0. Acidic or alkaline soil can hinder nutrient absorption.
- Water: Drinking water should have a pH of 6.5-8.5 to ensure safety.
- Food Safety: Foods like cheese and yogurt require low pH to maintain freshness and prevent bacterial growth.
- Aquatic Systems: Fish thrive in water with a pH of 6.5-9.0. Extreme levels can harm aquatic life.
Why pH is Critical in Various Industries
pH is a vital factor in many industries, ensuring environmental safety, food quality, and industrial processes. Whether it’s maintaining healthy aquatic ecosystems, improving crop growth, or ensuring the safety of drinking water, pH plays a central role in human health and environmental well-being. Monitoring and controlling pH is crucial to sustaining life and improving industrial outcomes.
FAQs
1. What is the ideal pH for water?
The ideal pH for drinking water is between 6.5 and 8.5 to ensure it is safe and free from harmful contaminants.
2. What is the pH range for most plants?
Most plants thrive in soil with a pH between 6.0 and 7.0, ensuring optimal nutrient availability.
3. How do pH levels affect fish?
Fish are sensitive to pH levels. A pH between 6.5 and 9.0 is ideal for fish, and extreme pH levels can harm their growth or reproduction.
4. Why is pH important in food preservation?
pH helps control microbial growth in food. Low pH prevents spoilage in dairy products and canned foods, ensuring food safety.
5. What industries use pH meters?
pH meters are widely used in industries like wastewater treatment, aquaculture, food processing, and chemical manufacturing for accurate pH measurement.
